The Maine Coon Cat
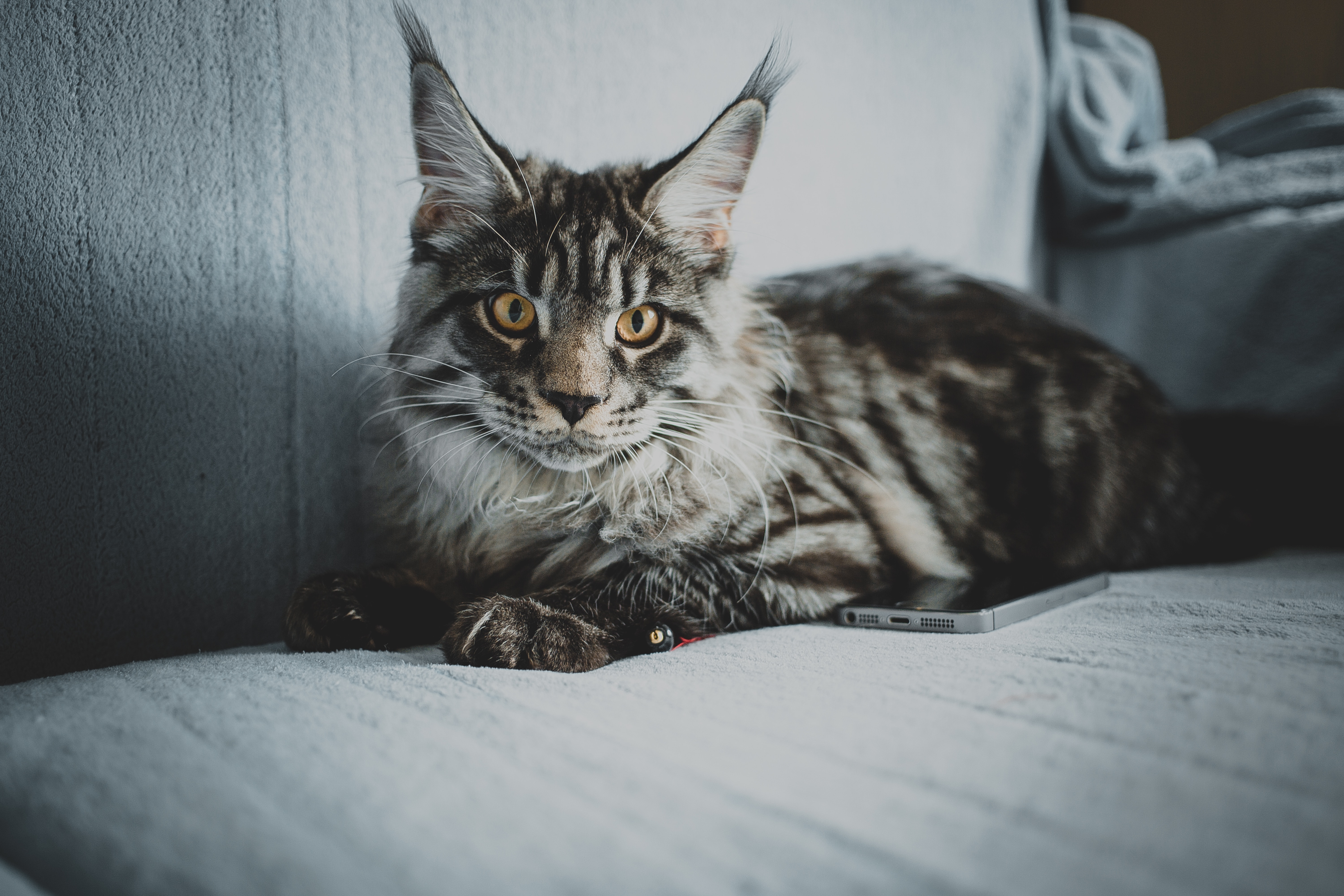

Physical Characteristics
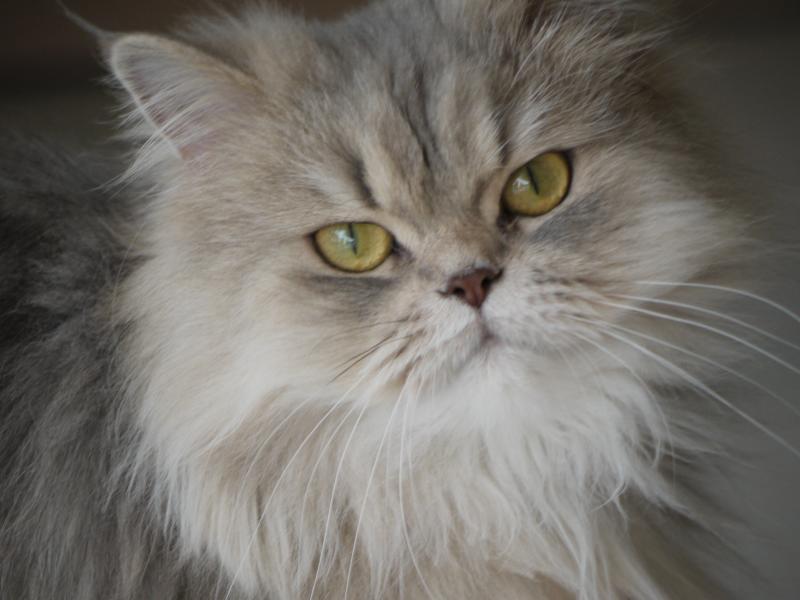
The Maine Coon is a huge feline that boasts a strong, muscular, and athletic physique, commensurate with its impressive dimensions. Its ears are sizeable, pointed, and held in a high and wide position, giving it an intelligent appearance. Additionally, its long and thick coat consists of a substantial, glossy, waterproof topcoat covering an undercoat, with charming tufts on the ears and paws. The Maine Coon's tail is remarkable and should be at least the same length as its body, enabling it to wrap around itself for additional warmth.
Personality
Maine Coon felines possess a loving disposition and are highly sociable, playful, and amiable creatures. They relish human interaction, making them ideal companions for those who appreciate having such a large cat around the house. One notable characteristic of Maine Coon cats is their charming and tranquil chirping noise.
The Maine Coon is a kind and well-balanced feline breed that possesses an incredibly sociable and affectionate personality towards its family. They exhibit a patient disposition that enables them to get along well with children, other cats, and even dogs. In addition, Maine Coons are exceptionally bright and have a dog-like demeanor that allows them to learn various tricks and commands.
History and Origins
The Maine Coon cat's predecessors were long-haired felines that served as diligent ship's cats, conceivably related to the Norwegian Forest cat. European sailors introduced them to Maine in the 1850s, and they mated with local shorthair cats, producing large, robustly built felines with semi-long fur and raccoon-like brush tails, hence the name Maine Coon. These cats evolved dense, heavy coats to survive harsh Maine winters and were highly valued for their exceptional hunting abilities. Maine Coon cat shows were already taking place in the 1860s, but it was not until the 1980s that these cats were imported into the UK.
The Siamese Cat

Physical Characteristics
Head is triangular in shape, and the ears are large and erect, contributing to an intelligent expression. Their eyes are almond-shaped and angled towards the nose, while the tail is straight, lengthy, and tapers towards the end. Their coat is fine and short, lying snugly against the body, and their coloration is pale with darker areas on the face, ears, legs, and tail, known as points.
The Siamese cat has two distinct appearances: the traditional type, which has a rounder body and an apple-shaped head, and the modern type, which is more slender and features a more wedge-shaped head.
Personality
The Siamese cat is renowned for its remarkable intelligence, affectionate nature, and assertive personality, making them the extroverts of the feline world. They are known to form strong bonds with one person and express their emotions vocally with a deep, loud voice referred to as a "meezer". As a result, the Siamese cat tends to have a polarizing effect, appealing to a specific kind of individual
Due to their inclination to develop strong bonds with their human companions, Siamese cats often experience separation anxiety and may benefit from being kept in pairs or households where someone is present most of the time.
History and Origins
The Siamese cat is one of the oldest recognized Asian breeds that originated from Siam, which is now known as Thailand. In the 19th century, they became increasingly popular in Europe and North America. In 1884, Pho and Mia, a pair of Siamese cats, were brought to Britain as a gift for Lilian Gould by the British Consul-General in Bangkok. Lilian Gould later co-founded the Siamese Cat Club in 1901
Siamese cats are renowned for their unique coloration, which has become so distinctive that the term "Siamese" now refers to various cats with the same color pattern. The pointed pattern of Siamese cats is caused by a mutation in the enzyme responsible for melanin production. This mutated enzyme is heat-sensitive, and it becomes active at lower temperatures found on the extremities of the body. As a result, the fur on those cooler areas appears much darker than the fur on the warmer parts, causing the distinct darker points. Siamese kittens are born either pure white or cream and gradually develop their color points as their fur grows and is affected by the enzyme.
The Sphynx Cat

Physical Characteristics
The most striking feature of the Sphynx cat is their absence of fur. However, the extent of their hairlessness varies, with some having a fine layer of hair all over, while others only have a light covering of hair on their extremities. Their lack of fur allows their bone structure and musculature to be easily seen. The Sphynx cat has a strong and elegant build, with long lines and slightly loose skin that forms wrinkles in some areas.
Their head is somewhat wedge-shaped, and they have large eyes and ears, long legs and tail, and rounded paws.
Personality
The Sphynx cat is an outgoing and energetic type, highly intelligent, curious, and affectionate. They are known for being friendly not only with their family but also with strangers, which makes them almost dog-like. These cats crave attention and enjoy being involved in everything you do. They may even get in the way or be a bit annoying at times, as they like to supervise and assist with everything from paperwork to cooking.
One unique trait of the Sphynx is their love for company, and they get along well with other animals, especially other Sphynx cats. However, this doesn't mean they will entertain themselves, and you can expect to have several Sphynx cats watching and helping you with everything.
Due to their hairlessness, the Sphynx cat likes warmth and can be quite cuddly. They love sneaking under the duvet and cuddling up with their owners.
History and Origins
The Sphynx cats, known for their hairlessness, were discovered in 1966 when a genetic mutation resulted in a hairless kitten in a domestic shorthair cat litter in Ontario, Canada. These cats have been present throughout history and were even kept by the Aztecs. The hairless gene is also present in other animals such as dogs, guinea pigs, mice and rats and has been selectively bred for in pet animals. Most of the modern Sphynx cats today can be traced back to two kittens found in Minnesota in 1975 and three kittens found in Toronto in 1978. While the Sphynx cat is often described as suitable for allergy sufferers, this is only true for the most hairless examples and only if the sufferer is allergic to hair and not cat saliva or dander.