Django Installation for Mac
Overview
These installation instructions are Mac-specific!
An installation script for Windows is located here.
Installation can be hard
-
The installation works for some people wihout any difficuly, but this is in fact unusual.
-
Many people have issues with the system path, version, etc., and the installation could become tedious. Have courage! The TAs and instructor and your classmates are here to help.
The commands below must be done one at a time. Make sure each one is successful before continuing to the next step. Please do not get hung up on version numbers. Use the latest version for any package you install!
Django Pre-requisites: Developer Tools and Homebrew
Open the Terminal, and do the following commands to install the pre-requisites for the Django libraries.
You should only need to do each of these commands once.
(You do not need to type the comments! These are here to explain what we’re doing on each line.)
# install the pre-requisites: developer tools sudo rm -rf /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools xcode-select --install # install homebrew, an installation manager for some of the packages we # need to install /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)" # this command will add brew to your system path: echo 'eval "$(/usr/local/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> ~/.zprofile eval "$(/usr/local/bin/brew shellenv)"
Note: if you get an error that brew is not found: you will need to discover where it was installed. Try this command:
which brew
It will show you the path in which the brew application is installed, for example:
/opt/homebrew/bin/brew. Use that directory path.
For good measure, let’s have brew install a version of python and pipenv:
brew install python brew install pipenv
Django Installation
We are creating a directory called django on the Desktop (for convenience).
You may use another location, but you need to remember what it is.
# create a django directory on the desktop, and change into that # directory. mkdir ~/Desktop/django cd ~/Desktop/django # create virtual environment, install django, and start virtual # environment shell pipenv install django pipenv shell
Starting a New Django Project
The following Terminal commands are used to start a new Django project. This assumes you have already changed into the django directory and started the virtual environment (see above).
You should only need to start the project once (for the entire semester/course)
You must call your project cs412, because that is the name that the configuration
file expects.
You MUST have a trailing period at the end of the diang-admin startproject line.
# create the django project in the current directory django-admin startproject cs412 .
Running the Django Development Server
The following Terminal commands are used to start the virtual environment (pipenv shell) run the Django server.
You will need to do these every time you open a new Terminal window. You will always need to start the development server before you can test anything in a web browser.
(You do not need to type the comments!)
# change into the django directory cd ~/Desktop/django # start the virtual environment shell pipenv shell # run the django development server python manage.py runserver
Did the installation work? You should seem some lines like this:
Starting development server at http://127.0.0.1:8000/ Quit the server with CONTROL-C.
Test it by opening a browser to http://127.0.0.1:8000/.
If it worked, you will see a “Welcome to Django” page:
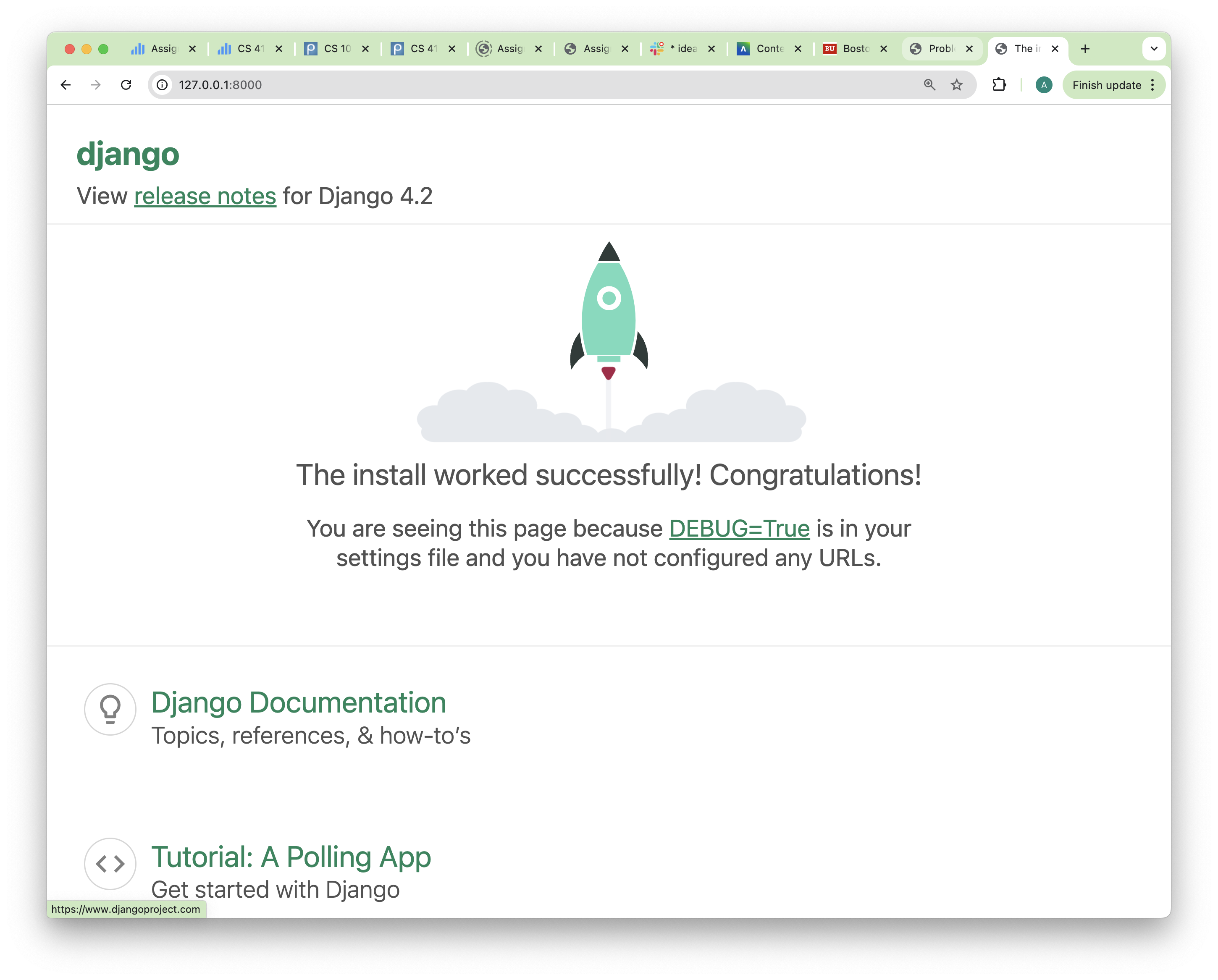
To stop the development server, use the keyboard sequence CONTROL-C.
Making and Applying Migrations
The following Terminal commands are used to make and apply database
changes to the Django development environment. This assumes you have
already changed into the django directory and started the virtual
environment (see above). You will need to do this when changes have been
made to the database models (this will be explained in part 2 of our
course).
(You do not need to type the comments!)
# create the migrations: the updates to the database models python manage.py makemigrations # apply the migrations python manage.py migrate
Do you have suggestions for improving these instructions?
Please share them with Aaron.
[cs_people]: http://cs-people.bu.edu [putty]: https://www.putty.org/ [django_running]: ../resources/django_running.png [installation_mac]: